Magnitude and Determinants of Nurses’ Perceived Stress and Burnout in a Tertiary Eye Hospital
Article Information
Wadha Al Shaibani2, Maha Al-Qahtani2, Enas AlAmri2, Rajiv Khandekar1*
1Department of Research, King Khaled Eye Specialist Hospital, Saudi Arabia
2Department of Nursing, King Khaled Eye Specialist Hospital, Saudi Arabia
*Corresponding Author: Rajiv Khandekar, Department of Research, King Khaled Eye Specialist Hospital, POB: 7191. Aruba road, Riyadh, Pin: 11462, Saudi Arabia
Received: 10 June 2020; Accepted: 07 July 2020; Published: 03 August 2020
Citation: Wadha Al Shaibani, Maha Al-Qahtani, Enas AlAmri, Rajiv Khandekar. Magnitude and Determinants of Nurses’ Perceived Stress and Burnout in a Tertiary Eye Hospital. Archives of Clinical and Medical Case Reports 4 (2020): 724-732.
View / Download Pdf Share at FacebookAbstract
Purpose: To assess the prevalence and determinants of stress among nurses of a tertiary eye hospital.
Methods: This cross sectional survey was held in 2019. Nursing staff of our eye hospital provided feedback about ten possible causes of stress in their profession and ten effects of stress on mental health of nurses. Five graded Liker scale was used to generate stress score. It was graded as none, mild, moderate and severe and correlated to the determinants.
Results: We surveyed 212 participants. Less than 4% of participants were Saudi nurses and 7% were male nurses. More than two thirds of nurses were in the profession for more than 10 years. The median stress score was -3.0 (IQR -9.0 ; +3.0) The stress was absent in 46 [21% (95% CI 16.1 ; 27.2)]. The stress was none in (46; 22%), mild (88; 22%), moderate (43; 20%) and severe (35; 16%). The occupation related stress was not associated significantly to gender (P = 0.5), nationality (P = 0.9) and rotation duties (P = 0.1). However it was more among nurses working in Inpatient units than other work station (P = 0.02). Overload of work, poor cooperation of eye patients, criticism of work, negligent coworkers and difficulty in interacting with eye doctors were leading causes of stress in more than two third of participating nurses.
Conclusions: One in four nurses of tertiary eye hospital expressed severe grade of stress. Measures to reduce the stress could improve mental health of nurses and patient care.
Keywords
Stress; Mental health; Nursing staff; Eye hospital
Stress articles, Mental health articles, Nursing staff articles, Eye hospital articles
Stress articles Stress Research articles Stress review articles Stress PubMed articles Stress PubMed Central articles Stress 2023 articles Stress 2024 articles Stress Scopus articles Stress impact factor journals Stress Scopus journals Stress PubMed journals Stress medical journals Stress free journals Stress best journals Stress top journals Stress free medical journals Stress famous journals Stress Google Scholar indexed journals Mental health articles Mental health Research articles Mental health review articles Mental health PubMed articles Mental health PubMed Central articles Mental health 2023 articles Mental health 2024 articles Mental health Scopus articles Mental health impact factor journals Mental health Scopus journals Mental health PubMed journals Mental health medical journals Mental health free journals Mental health best journals Mental health top journals Mental health free medical journals Mental health famous journals Mental health Google Scholar indexed journals Nursing staff articles Nursing staff Research articles Nursing staff review articles Nursing staff PubMed articles Nursing staff PubMed Central articles Nursing staff 2023 articles Nursing staff 2024 articles Nursing staff Scopus articles Nursing staff impact factor journals Nursing staff Scopus journals Nursing staff PubMed journals Nursing staff medical journals Nursing staff free journals Nursing staff best journals Nursing staff top journals Nursing staff free medical journals Nursing staff famous journals Nursing staff Google Scholar indexed journals Thymic carcinoma articles Thymic carcinoma Research articles Thymic carcinoma review articles Thymic carcinoma PubMed articles Thymic carcinoma PubMed Central articles Thymic carcinoma 2023 articles Thymic carcinoma 2024 articles Thymic carcinoma Scopus articles Thymic carcinoma impact factor journals Thymic carcinoma Scopus journals Thymic carcinoma PubMed journals Thymic carcinoma medical journals Thymic carcinoma free journals Thymic carcinoma best journals Thymic carcinoma top journals Thymic carcinoma free medical journals Thymic carcinoma famous journals Thymic carcinoma Google Scholar indexed journals carcinoma articles carcinoma Research articles carcinoma review articles carcinoma PubMed articles carcinoma PubMed Central articles carcinoma 2023 articles carcinoma 2024 articles carcinoma Scopus articles carcinoma impact factor journals carcinoma Scopus journals carcinoma PubMed journals carcinoma medical journals carcinoma free journals carcinoma best journals carcinoma top journals carcinoma free medical journals carcinoma famous journals carcinoma Google Scholar indexed journals treatment articles treatment Research articles treatment review articles treatment PubMed articles treatment PubMed Central articles treatment 2023 articles treatment 2024 articles treatment Scopus articles treatment impact factor journals treatment Scopus journals treatment PubMed journals treatment medical journals treatment free journals treatment best journals treatment top journals treatment free medical journals treatment famous journals treatment Google Scholar indexed journals CT articles CT Research articles CT review articles CT PubMed articles CT PubMed Central articles CT 2023 articles CT 2024 articles CT Scopus articles CT impact factor journals CT Scopus journals CT PubMed journals CT medical journals CT free journals CT best journals CT top journals CT free medical journals CT famous journals CT Google Scholar indexed journals surgery articles surgery Research articles surgery review articles surgery PubMed articles surgery PubMed Central articles surgery 2023 articles surgery 2024 articles surgery Scopus articles surgery impact factor journals surgery Scopus journals surgery PubMed journals surgery medical journals surgery free journals surgery best journals surgery top journals surgery free medical journals surgery famous journals surgery Google Scholar indexed journals Eye articles Eye Research articles Eye review articles Eye PubMed articles Eye PubMed Central articles Eye 2023 articles Eye 2024 articles Eye Scopus articles Eye impact factor journals Eye Scopus journals Eye PubMed journals Eye medical journals Eye free journals Eye best journals Eye top journals Eye free medical journals Eye famous journals Eye Google Scholar indexed journals caval syndrome articles caval syndrome Research articles caval syndrome review articles caval syndrome PubMed articles caval syndrome PubMed Central articles caval syndrome 2023 articles caval syndrome 2024 articles caval syndrome Scopus articles caval syndrome impact factor journals caval syndrome Scopus journals caval syndrome PubMed journals caval syndrome medical journals caval syndrome free journals caval syndrome best journals caval syndrome top journals caval syndrome free medical journals caval syndrome famous journals caval syndrome Google Scholar indexed journals
Article Details
1. Introduction
Health care providers face work related stress to a large extent and it is likely to increase in coming years. It also affects mental health of nurses, patient care negatively. It also indirectly has financial impact on the organization [1]. Therefore estimating the magnitude of stress, stressors and impact of intervention strategies to reduce stress and burnout among nursing staff are crucial [2, 3, 4]. A number of studies revealing amount of stress especially burnout (severe grades of stress) among nursing staff of different workplace. Nurses of oncology department, Intensive care units, hemodialysis units and old age care centers have experienced stress and burnout and even suggested remedial measures to reduce the negative effects of stress [5, 6, 7, 8]. Professionals related to eye care in Canada reported 35% stress and burnout [9]. Nearly 70% to 80% Ophthalmologists of USA and European continent felt occupational stress mainly due to patient care and hospital administrative issues [10]. As many as 53% Optometrists expressed stress during their work mainly due to work overload and clinical tasks [11]. Physical symptoms of stress include chronic headache, neck and back pain. Among 50% of eye care professionals, neck and back pain was work related [12]. To the best of our knowledge, stress and burnout among nursing staff working for eye care has not been studied. Ours is a tertiary eye care hospital catering services to cases referred and with advanced complicated eye diseases in Saudi Arabia. We present the magnitude and determinants of work related stress among nursing staff of an eye hospital of central Saudi Arabia.
2. Methods
The institution research board (IRB) approved of this survey. All nurses working in the institution were invited to participate in this survey in 2019. Written consent was obtained from each participant. The nursing staff on annual leave during 2 weeks of survey were excluded. We assumed that among 400 nursing staff in eye hospital the stress of moderate to severe grade is prevalent in 30% nurses as noted among oncology nurses [4]. To achieve 95% confidence interval, 5% acceptable error margin and 1.2 factor of clustering by work station, we need to recruit randomly selected at least 215 nurses need to be surveyed. We used Open epi software to calculate the sample size for this study [13]. Two nursing staff and one clinical coordinator were the field staff. The pretested data collection form was used. The demographic information included age, nationality and gender. Work related information included number of years in institution and in nursing profession, current workstation and rotation in duties. Participants were asked about their perception of possible component of nursing work that can cause stress. Participants were asked to tick all stressors. There were ten possible perceived effects of stress on working of nursing staff. Participants were given one of the five option using Likert scale. The fully agree was given +2 score. Agree; +1 score, fully disagree of -2, disagree -1 and ‘Cannot say’ was awarded ‘0’ the sum total of all ten responses was done to conclude each nurses perception. The total score was then classified as: none (<-10 score), mild (-1 to -10), moderate (0 to +9) and severe (>11). The grades of stress were then associated to demographic and work related factors. The data was collected on pretested data collection form. It was then transferred in spreadsheet of Microsoft Access®. After cleaning the data using frequency and consistency checks, it was transferred into spreadsheet of Statistical Package for Social studies (SPSS 26) (IMB, Chicago, USA). The qualitative variables were presented as frequency and percentage proportion. The quantitative variable of normal distribution were presented as mean and standard deviation. Those not normally distributed were presented as median and inter quartile range. To compare the outcomes in two subgroups we presented difference of mean, 95% Confidence interval and two sided P value. A P value of <0.005 was considered as statistically significant.
3. Results
We surveyed 212 nursing of a tertiary eye hospital to inquire about stress and burnout felt by them as part of their profession. The demographic profile of the participants is given in Table 1. Less than 4% of participants were Saudi nurses and 7% were male nurses. More than two thirds of nurses were in the profession for more than 10 years. The median stress score was -3.0 (IQR -9.0 ; +3.0) The stress was absent in 46 [21% (95% CI 16.1 ; 27.2)], the grades of stress perceived by nurses is given in Figure 1. We grouped moderate and severe grade of nurse perceived stress as ‘worth noting’ while none and mild stress was grouped as ‘negligent’. We associated different demographic and nurse working related variables to stress grade. Table 2. None of the demographic and duration of nursing work were associated to stress of statistically significant level. Nurses perceived causes of stress & burnout among ophthalmic nurses is given in Table 3. Overload of work, poor cooperation of eye patients, criticism of work, negligent coworkers and difficulty in interacting with eye doctors were leading causes of stress in more than two third of participating nurses. We reviewed work station by four grades of stress score. Among five type of work station the stress level variation was statistically significant. (c2 = 17.6, DF= 9, P = 0.04). The level of stress among nursing staff of different health sector in published literature is given in Table 4.
|
Age (years) |
Median Inter quartile rage (IQR) |
36 32 :43 |
|
|
Number of years in KKESH |
Median IQR |
7 3.25 :12 |
|
|
Number of years in nursing |
Median IQR |
12.5 8 : 20 |
|
|
Number |
Percentage |
||
|
Nationality |
Saudi Non-Saudi |
8 204 |
3.8 96.2 |
|
Gender |
Male Female |
14 198 |
6.6 93.4 |
|
Rotation duties |
Yes No |
75 137 |
35.4 64.6 |
|
Work station |
Out-patient In-patient Short stay unit Operation theater Administration Recovery room unit Anesthesia Emergency Employee health |
46 80 13 19 2 16 6 27 3 |
21.7 37.7 6.1 9.0 0.9 7.5 2.8 12.7 1.4 |
Table 1: Nurses perceived occupational stress and burnout at eye hospital.
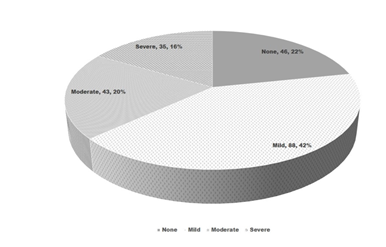
Figure 1: distribution of stress among nurses of eye hospital by grades.
|
|
Significant stress & burnout (N = 78) |
Insignificant stress & burnout (N = 134) |
Validation |
|||
|
Number |
Percentage |
Number |
Percentage |
|||
|
Gender |
Male Female |
4 74 |
5.1 94.9 |
10 124 |
7.5 92.5 |
OR = 0.7 (0.2 ; 2.2) P = 0.5 |
|
Nationality |
Saudi Non Saudi |
3 75 |
3.8 96.2 |
5 129 |
3.7 96.3 |
OR = 1.2 (95% CI 0.2 ; 4.4) P = 0.9 |
|
Rotation duties |
Yes No |
56 22 |
71.8 28.2 |
82 52 |
61.2 38.8 |
OR = 1.6 (95% CI 0.9 ; 3.0) P = 0.1 |
|
Work station |
Out-patient In-patient Short stay unit Operation theater Other |
21 35 2 6 14 |
26.9 44.9 2.6 7.7 17.9 |
25 45 14 13 37 |
18.7 33.6 10.4 9.7 27.6 |
c2 = 5.5 Df = 5 P = 0.02 |
|
Age |
Mean SDV |
37.5 9.1 |
38.6 9.9 |
0.96 (95% CI -1.3 ; 3.2) P = 0.4 |
||
|
Years in nursing |
Mean SDV |
14.2 7.1 |
14.3 9.1 |
0.1 (-2.2 ; +2.3) P = 0.96 |
||
Table 2: Factors associated to stress and burnout among nurses working in a tertiary eye hospital.
|
S no |
Cause |
Number |
Percentage |
|
1 |
Work overload |
186 |
87.7 |
|
2 |
Uncooperative patients |
164 |
77.4 |
|
3 |
Criticism of work performed |
136 |
64.2 |
|
4 |
Negligent co-workers |
139 |
65.6 |
|
5 |
Lack of support of supervisors |
127 |
59.9 |
|
6 |
Difficulties with doctors |
137 |
64.6 |
|
7 |
Newer tasks allotted without proper practical training |
122 |
57.5 |
|
8 |
Tasks related to electronic health records |
114 |
53.8 |
|
9 |
Lack of time for creative thinking |
114 |
53.8 |
|
10 |
Family & personal problems brought to work station |
71 |
33.5 |
Table 3: Nurses perceived causes of stress & burnout among ophthalmic nurses.
|
No |
Authors |
Category |
Year |
Sample |
Highlight |
Reference |
|
1 |
Canadas-De et al |
Oncology nurses |
2018 |
9,959 |
Emotional exhaustion: 30% (95% CI 26 ; 33) Depersonalization 15% (95% CI 9 ; 23) |
7 |
|
2 |
Parola V et al |
Palliative care nurses |
2017 |
1,406 |
Burnout: 17.3%, Emotional exhaustion (19.5%), Depersonalization (8.2%) |
11 |
|
3 |
Nla RG |
Emergency nurses |
2015 |
150 60 nurses |
Stress 11% , intense anxiety 17% |
14 |
|
4 |
Heishamn et al |
Critical ward nurses |
2015 |
3,043 |
46.2% had significant stress score Male, unmarried, time of shift and years of nursing were associated with stress level |
15 |
|
5 |
Mosadeghrad AM |
Hospital nurses |
2013 |
296 |
33% had high grade of stress in Iran Job leaving 35% |
16 |
|
6 |
Bhatia et al |
Hospital nurses |
2010 |
87 |
87% had stress in North India |
17 |
|
7 |
Wang IL et al |
Public health nurses |
2002 |
167 |
Occupational Stressors Scale: 159.4 ±29.2. Workload, personal responsibility stressors |
18 |
|
8 |
Present study |
Eye hospital nurses |
2019 |
212 |
- |
Table 4: Stress and burnout among health care providers.
4. Discussion
One fourth of nurses working in eye hospital perceived that they do not face stress while nearly one in six nurse faces severe grade of stress. The variation of perceived stress among nurses working in different work station was significant. Workload, poor cooperation of patients and criticism of higher authorities were main causes of stress among nurses of eye hospital. This is perhaps first such survey of nurses of a tertiary eye hospital. The magnitude of stress suggest that nurses of eye hospital face similar extent of stress and stressors. Giving opportunity to express about their problems and stress is in one way of addressing this mental health issue. This also gives area that need more focus. Eye care services in a tertiary hospital has undergone dramatic transition in last few decades. Majority of patients except ocular trauma, pediatric surgical cases and chronic retinal conditions that need postoperative supervised care, are managed as day care patients. Nursing care also has changed accordingly. Advent of electronic health record in 21st century resulted in additional job responsibilities which nurses adopted very well. While comparing the stress level of nurses of eye hospital to the other published studies showing prevalence of stress and burnout, it is noted that those providing terminal illness related patient care like oncology units, intensive care unit and palliative care unit, the stress level was lower in our cohort [4, 7, 11, 14-19]. We did not find gender difference in stress level among nurses. This could be due to small sample of males in our study. Female gender have been shown higher level of occupational stress compared to male nurses [15]. Coping up with stress could be better among males compared to Iranian nurses. In our study nurses of inpatient department expressed higher risk of stress compared to nurses of outpatient unit, administration and anesthetic nurses. Most of the eye care in our institute is through ‘Day Care’ but patients with ocular trauma and patients with chronic eye diseases needing constant monitoring are admitted. Thus nurses who are facing more workload, patient and their relatives interaction for a longer time and strict administrative protocols the ward nurses have to face compared to nurses of other work station could explain this variation. Usually nurses of operation theatre experience more stress and even blamed for errors [20]. But anesthetic nurses in our institute work under constant supervision of consultant anesthetist and are not liable to patient’s condition during surgery. In our ophthalmology hospital, intensive care unit does not exist. Patients with high mortality risks after surgery are shifted to other hospital for management in ICU. The nurses in such ICU have very high emotional exhaustion (70%) and 7% rate of burnout [21]. The workload was the leading cause of stress among nursing staff of eye hospital. This was a confirmed stressor in a study from USA. Researcher sin this study noted that an increase in patient nurse ratio increases the risk of stress and dissatisfaction among nurses [22]. Non appreciation and criticism by higher authorities was perceived stressor among nurses in our study. This was also noted and appreciating outstanding performance of nurses was recommended strategy to reduce stress in a study from Jordan [23]. Poor cooperation of patient was reported stressor by a large number of nurses in our study. Limited number of native nurses, inability to speak local language fluently could be the reason for poor communication with patients resulting in this observed stressor. There were few limitations in present study. Male nurses and Saudi nurses were very few and therefore their influence on stress level could not be established conclusively. This being a cross sectional study, occupation related factors could not have special relationship with stress level as perceived by the nurses. In a study where perceived burnout and causes are collected, possible solution should have been also inquired. This being a part of a larger study with primary focus on Electronic Health Record related stress, solutions were inquired for this issue only. Nursing staff in an eye hospital are special manpower as part of mid-level eye care professionals. In absence of large scale training centers for ophthalmic nursing, huge efforts are made to train general nurses in eye care of tertiary level. Minimizing attrition of such trained staff is crucial. Negative effects on mental health of such nurses which could cause rapid turnover, dissatisfaction and even quality of care must be minimized.
Funding
None
Conflict of Interest
None
References
- Zeller JM, Levin PF. Mindfulness interventions to reduce stress among nursing personnel: an occupational health perspective. Workplace Health Saf 61 (2013): 85-89.
- Romppanen J, Häggman-Laitila A. Interventions for nurses' well-being at work: a quantitative systematic review. J Adv Nurs 73 (2017): 1555-1569.
- Delgado C, Upton D, Ranse K, et al. Nurses' resilience and the emotional labour of nursing work: An integrative review of empirical literature. Int J Nurs Stud 70 (2017): 71-88.
- Gómez-Urquiza JL, Aneas-López AB, Fuente-Solana EI, et al. Prevalence, Risk Factors, and Levels of Burnout Among Oncology Nurses: A Systematic Review. Oncol Nurs Forum 43 (2016): E104-E120.
- Cañadas-De la Fuente GA, Gómez-Urquiza JL, Ortega-Campos EM, et al. Prevalence of burnout syndrome in oncology nursing: A meta-analytic study. Psychooncology 27 (2018): 1426-1433.
- Doede M, Trinkoff AM, Gurses AP. Neonatal Intensive Care Unit Layout and Nurses' Work. HERD11 (2018): 101-118.
- Hayes B, Bonnet A. Job satisfaction, stress and burnout associated with haemodialysis nursing: a review of literature. J Ren Care 36 (2010): 174-179.
- Le Gall JR, Azoulay E, Embriaco N, et al. Burn out syndrome among critical care workers. Bull Acad Natl Med 195 (2011): 389-397.
- Viviers S, Lachance L, Maranda MF, et al. Burnout, psychological distress, and overwork: the case of Quebec's ophthalmologists. Canadian Journal of Ophthalmology 43 (5): 535-546.
- Drews C, Celano M, Plager DA, et al. Parenting stress among caregivers of children with congenital cataracts. Journal of American Association for Pediatric Ophthalmology and Strabismus 7 (2003): 244-250.
- Long J, Burgess?Limerick R, Stapleton F. What do clinical optometrists like about their job?. Clinical and Experimental Optometry 96 (2013): 460-466.
- Al-Marwani Al-Juhani M, Khandekar R, Al-Harby M, et al. Neck and upper back pain among eye care professionals. Occupational Medicine 65 (2015): 753-757.
- Dean AG, Sullivan KM, Soe MM. OpenEpi: Open Source Epidemiologic Statistics for Public Health (2019).
- Le Gall JR, Azoulay E, Embriaco N, et al. Burn out syndrome among critical care workers. Bull Acad Natl Med 195 (2011): 389-397.
- Nia RG. Evaluating the degree of stress, anxiety, and depression among the emergency personnel in Kerman University of medical sciences. Sci Res Essays 2 (2016): 1-6.
- Hashemian SM, Farzanegan B, Fathi M, et al. Stress among Iranian nurses in critical wards. Iranian Red Crescent Medical Journal 17 (2015).
- Mosadeghrad AM. Occupational stress and turnover intention: implications for nursing management. International journal of health policy and management 1 (2013): 169.
- Bhatia N, Kishore J, Anand T, et al. Occupational stress amongst nurses from two tertiary care hospitals in Delhi. Australasian Medical Journal (Online) 3 (2010): 731.
- Lee I, Wang HH. Perceived occupational stress and related factors in public health nurses. The journal of nursing research: JNR 10 (2002): 253-260.
- Zhou H, Gong YH. Relationship between occupational stress and coping strategy among operating theatre nurses in C hina: a questionnaire survey. Journal of Nursing Management 23 (2015): 96-106.
- Van Mol MM, Kompanje EJ, Benoit DD, etal. The prevalence of compassion fatigue and burnout among healthcare professionals in intensive care units: a systematic review. PloS one 10 (2015): e0136955.
- Aiken LH, Clarke SP, Sloane DM, et al. Hospital nurse staffing and patient mortality, nurse burnout, and job dissatisfaction. Jama 288 (2002): 1987-1993.
- AbuAlRub RF, AL?ZARU IM. Job stress, recognition, job performance and intention to stay at work among Jordanian hospital nurses. Journal of nursing management 16 (2008): 227-236.


 Impact Factor: * 3.1
Impact Factor: * 3.1 CiteScore: 2.9
CiteScore: 2.9  Acceptance Rate: 11.01%
Acceptance Rate: 11.01%  Time to first decision: 10.4 days
Time to first decision: 10.4 days  Time from article received to acceptance: 2-3 weeks
Time from article received to acceptance: 2-3 weeks 
