Usefulness of the Echo-Guided Parasternal Tunneling for the Subcutaneous Implantable Cardioverter-Defibrillator Implantation In High Body Mass Index Patient
Article Information
Shingo Sasaki, MD, PhD*, Kimitaka Nishizaki, MD, PhD, Yuji Ishida, MD, PhD, Yuichi Toyama, MD, PhD, Takashi Yokota, MD, PhD, Hirofumi Tomita, MD, PhD
Department of Cardiology and Nephrology, Hirosaki University Graduate School of Medicine, Hirosaki, Japan
*Corresponding Author: Shingo Sasaki, MD, PhD, Department of Cardiology and Nephrology, Hirosaki University Graduate School of Medicine, 5 Zaifu-cho, Hirosaki, 036-8562, Japan
Received: 23 October 2020; Accepted: 02 November 2020; Published: 30 November 2020
Citation: Shingo Sasaki, Kimitaka Nishizaki, Yuji Ishida, Yuichi Toyama, Takashi Yokota, Hirofumi Tomita. Usefulness of the Echo-Guided Parasternal Tunneling for the Subcutaneous Implantable Cardioverter-Defibrillator Implantation In High Body Mass Index Patient. Archives of Clinical and Medical Case Reports 4 (2020): 1116-1118.
View / Download Pdf Share at FacebookAbstract
Successful implantation of the subcutaneous implantable cardioverter-defibrillator (S-ICD) (EMBLEM, Boston Scientific, Marlborough, Massachusetts, USA) in highly obese patients represented by high body mass index (BMI) is extremely difficult due to inappropriate parasternal tunneling. We attempted echo-guided parasternal tunneling during S-ICD implantation for a 59-year-old high BMI patient and succeeded in placing the lead on the optimal position.
Keywords
S-ICD; Echo-guided parasternal tunneling; High BMI
S-ICD articles; Echo-guided parasternal tunneling articles; High BMI articles
S-ICD articles S-ICD Research articles S-ICD review articles S-ICD PubMed articles S-ICD PubMed Central articles S-ICD 2023 articles S-ICD 2024 articles S-ICD Scopus articles S-ICD impact factor journals S-ICD Scopus journals S-ICD PubMed journals S-ICD medical journals S-ICD free journals S-ICD best journals S-ICD top journals S-ICD free medical journals S-ICD famous journals S-ICD Google Scholar indexed journals Echo-guided parasternal tunneling articles Echo-guided parasternal tunneling Research articles Echo-guided parasternal tunneling review articles Echo-guided parasternal tunneling PubMed articles Echo-guided parasternal tunneling PubMed Central articles Echo-guided parasternal tunneling 2023 articles Echo-guided parasternal tunneling 2024 articles Echo-guided parasternal tunneling Scopus articles Echo-guided parasternal tunneling impact factor journals Echo-guided parasternal tunneling Scopus journals Echo-guided parasternal tunneling PubMed journals Echo-guided parasternal tunneling medical journals Echo-guided parasternal tunneling free journals Echo-guided parasternal tunneling best journals Echo-guided parasternal tunneling top journals Echo-guided parasternal tunneling free medical journals Echo-guided parasternal tunneling famous journals Echo-guided parasternal tunneling Google Scholar indexed journals Echo articles Echo Research articles Echo review articles Echo PubMed articles Echo PubMed Central articles Echo 2023 articles Echo 2024 articles Echo Scopus articles Echo impact factor journals Echo Scopus journals Echo PubMed journals Echo medical journals Echo free journals Echo best journals Echo top journals Echo free medical journals Echo famous journals Echo Google Scholar indexed journals tunneling articles tunneling Research articles tunneling review articles tunneling PubMed articles tunneling PubMed Central articles tunneling 2023 articles tunneling 2024 articles tunneling Scopus articles tunneling impact factor journals tunneling Scopus journals tunneling PubMed journals tunneling medical journals tunneling free journals tunneling best journals tunneling top journals tunneling free medical journals tunneling famous journals tunneling Google Scholar indexed journals High BMI articles High BMI Research articles High BMI review articles High BMI PubMed articles High BMI PubMed Central articles High BMI 2023 articles High BMI 2024 articles High BMI Scopus articles High BMI impact factor journals High BMI Scopus journals High BMI PubMed journals High BMI medical journals High BMI free journals High BMI best journals High BMI top journals High BMI free medical journals High BMI famous journals High BMI Google Scholar indexed journals treatment articles treatment Research articles treatment review articles treatment PubMed articles treatment PubMed Central articles treatment 2023 articles treatment 2024 articles treatment Scopus articles treatment impact factor journals treatment Scopus journals treatment PubMed journals treatment medical journals treatment free journals treatment best journals treatment top journals treatment free medical journals treatment famous journals treatment Google Scholar indexed journals CT articles CT Research articles CT review articles CT PubMed articles CT PubMed Central articles CT 2023 articles CT 2024 articles CT Scopus articles CT impact factor journals CT Scopus journals CT PubMed journals CT medical journals CT free journals CT best journals CT top journals CT free medical journals CT famous journals CT Google Scholar indexed journals surgery articles surgery Research articles surgery review articles surgery PubMed articles surgery PubMed Central articles surgery 2023 articles surgery 2024 articles surgery Scopus articles surgery impact factor journals surgery Scopus journals surgery PubMed journals surgery medical journals surgery free journals surgery best journals surgery top journals surgery free medical journals surgery famous journals surgery Google Scholar indexed journals Cardioverter articles Cardioverter Research articles Cardioverter review articles Cardioverter PubMed articles Cardioverter PubMed Central articles Cardioverter 2023 articles Cardioverter 2024 articles Cardioverter Scopus articles Cardioverter impact factor journals Cardioverter Scopus journals Cardioverter PubMed journals Cardioverter medical journals Cardioverter free journals Cardioverter best journals Cardioverter top journals Cardioverter free medical journals Cardioverter famous journals Cardioverter Google Scholar indexed journals Defibrillator articles Defibrillator Research articles Defibrillator review articles Defibrillator PubMed articles Defibrillator PubMed Central articles Defibrillator 2023 articles Defibrillator 2024 articles Defibrillator Scopus articles Defibrillator impact factor journals Defibrillator Scopus journals Defibrillator PubMed journals Defibrillator medical journals Defibrillator free journals Defibrillator best journals Defibrillator top journals Defibrillator free medical journals Defibrillator famous journals Defibrillator Google Scholar indexed journals
Article Details
1. Case Report
Successful implantation of the subcutaneous implantable cardioverter-defibrillator (S-ICD) (EMBLEM, Boston Scientific, Marlborough, Massachusetts, USA) in highly obese patients represented by high body mass index (BMI) is extremely difficult due to inappropriate parasternal tunneling. Inappropriate parasternal tunneling, which defined by the existence of fat tissue between the shock-coil and surface of the sternum, has been shown to increase shock impedance and reduce the successful defibrillation [1, 2].
A 59-year-old male with left ventricular systolic dysfunction after aortic and mitral valve replacement underwent S-ICD implantation by two-incision technique [3]. The procedure was performed under conscious sedation using continuous intravenous infusion of midazolam with intermittent intravenous administration of fentanyl, and local anesthesia. The S-ICD generator was placed in intermuscular space between the serratus anterior muscle and the latissimus dorsi muscle via a lateral sub-mammary incision. Because the patient was highly obese (BMI 30.4 kg/m2) and the surface of the sternum was not fully recognized due to large amount of subcutaneous fat, we attempted a novel echo-guided parasternal tunneling using the electrode delivery system (EDS 4712, Boston Scientific, Marlborough, Massachusetts, USA) (Figure 1). The transthoracic echo (Vivid iq, GE healthcare) demonstrated subcutaneous structure such as sparse fat tissue, curved surface of sternum, and sternocostal joints. The tip of the insertion tool was also visible (Figure 2).
We confirmed that the tip of the insertion tool was in contact with the surface of the sternum or sternocostal joints by echo and succeeded deep tunneling accurately. Defibrillation test was performed during the procedure and successfully terminated by a single 65 J shock. The time to shock was 13.2 seconds and the post-shock impedance was 65 ohms.
In the S-ICD implantation, achievement of the posterior generator position and accurate substernal tunneling, which defined as a lack of intervening fat between the coil and/or the generator and the underlying fascia, are expected to be predictors of successful defibrillation. Therefore, echo-guided parasternal tunneling may be a useful method for S-ICD implantation in high BMI patients.
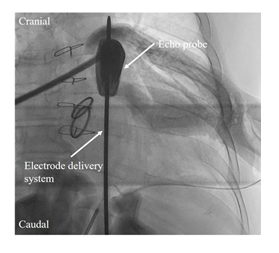
Figure 1: Fluoroscopic image during echo-guided parasternal tunneling using the electrode delivery system.
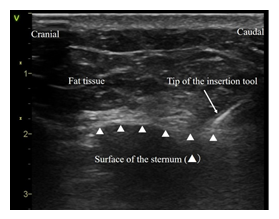
Figure 2: Demonstration of subcutaneous structure such as sparse fat tissue, curved surface of sternum, and sternocostal joints by transthoracic echo.
2. Sources of Funding
There was no financial support for this study.
3. Conflict of Interest
Dr. Shingo Sasaki has received research grant supports from Medtronic Japan Co., Ltd. and Fukuda Denshi Kita-tohoku Hanbai Co., Ltd. and BIOTRONIK Japan Co., Ltd. Dr. Shingo Sasaki has received scholarship donation from Japan Lifeline Co., Ltd and Boston Scientific Japan Co., Ltd. The all other authors have no relevant disclosures.
References
- Heist EK, Belalcazar A, Stahl W, et al. Determinants of subcutaneous implantable cardioverter-defibrillator efficacy: a computer modeling study. JACC Clin Electrophysiol 3 (2017): 405-414.
- Amin AK, Gold MR, Burke MC, et al. Factors associated with high-voltage impedance and subcutaneous implantable defibrillator ventricular fibrillation conversion success. Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol (2019): 12:e006665.
- Knops RE, Olde Nordkamp LR, de Groot JR, Wilde AA. Two-incision technique for implantation of the subcutaneous implantable cardioverter-defibrillator. Heart Rhythm 10 (2013): 1240-1243.


 Impact Factor: * 3.1
Impact Factor: * 3.1 CiteScore: 2.9
CiteScore: 2.9  Acceptance Rate: 11.01%
Acceptance Rate: 11.01%  Time to first decision: 10.4 days
Time to first decision: 10.4 days  Time from article received to acceptance: 2-3 weeks
Time from article received to acceptance: 2-3 weeks 
